FAQ
Frequently asked questions and answers about BitVPN
Bitcoin is an innovative payment network and a new kind of money.
Bitcoin uses peer-to-peer technology to operate with no central authority or banks; managing transactions and the issuing of bitcoins is carried out collectively by the network. Bitcoin is open-source; its design is public, nobody owns or controls Bitcoin and everyone can take part. Through many of its unique properties, Bitcoin allows exciting uses that could not be covered by any previous payment system.
Bitcoin uses peer-to-peer technology to operate with no central authority or banks; managing transactions and the issuing of bitcoins is carried out collectively by the network. Bitcoin is open-source; its design is public, nobody owns or controls Bitcoin and everyone can take part. Through many of its unique properties, Bitcoin allows exciting uses that could not be covered by any previous payment system.
Bitcoin is the simplest way to exchange money at very
low cost.
Mobile payments made easy
Bitcoin on mobiles allows you to pay with a simple two step scan-and-pay. No need to swipe your card, type a PIN, or sign anything. And all you need to do to receive Bitcoin payments is to display the QR code in your Bitcoin wallet app and let your friend scan your mobile, or touch the two phones together (using NFC radio technology).
Security and control over your money
Bitcoin transactions are secured by military grade cryptography. Nobody can charge you money or make a payment on your behalf. So long as you take the required steps to protect your wallet, Bitcoin can give you control over your money and a strong level of protection against many types of fraud.
Works everywhere, anytime
Just like with email, you don't need to force your family to use the same software or the same service providers. Just let them stick to their own favorites. No problem there; they are all compatible as they use the same open technology. The Bitcoin network never sleeps, even on holidays!
Fast international payments
Bitcoins can be transferred from Africa to Canada in 10 minutes. There is no bank to slow down the process, level outrageous fees, or freeze the transfer. You can pay your neighbors the same way as you can pay a member of your family in another country.
Zero or low fees
Bitcoin allows you to send and receive payments at very low cost. Except for special cases like very small payments, there is no enforced fee. It is however recommended to pay a higher voluntary fee for faster confirmation of your transaction and to remunerate the people who operate the Bitcoin network.
Protect your identity
With Bitcoin, there is no credit card number that some malicious actor can collect in order to impersonate you. In fact, it is even possible to send a payment without revealing your identity, almost just like with real money. You should however take note that some effort can be required to protect your privacy.
Mobile payments made easy
Bitcoin on mobiles allows you to pay with a simple two step scan-and-pay. No need to swipe your card, type a PIN, or sign anything. And all you need to do to receive Bitcoin payments is to display the QR code in your Bitcoin wallet app and let your friend scan your mobile, or touch the two phones together (using NFC radio technology).
Security and control over your money
Bitcoin transactions are secured by military grade cryptography. Nobody can charge you money or make a payment on your behalf. So long as you take the required steps to protect your wallet, Bitcoin can give you control over your money and a strong level of protection against many types of fraud.
Works everywhere, anytime
Just like with email, you don't need to force your family to use the same software or the same service providers. Just let them stick to their own favorites. No problem there; they are all compatible as they use the same open technology. The Bitcoin network never sleeps, even on holidays!
Fast international payments
Bitcoins can be transferred from Africa to Canada in 10 minutes. There is no bank to slow down the process, level outrageous fees, or freeze the transfer. You can pay your neighbors the same way as you can pay a member of your family in another country.
Zero or low fees
Bitcoin allows you to send and receive payments at very low cost. Except for special cases like very small payments, there is no enforced fee. It is however recommended to pay a higher voluntary fee for faster confirmation of your transaction and to remunerate the people who operate the Bitcoin network.
Protect your identity
With Bitcoin, there is no credit card number that some malicious actor can collect in order to impersonate you. In fact, it is even possible to send a payment without revealing your identity, almost just like with real money. You should however take note that some effort can be required to protect your privacy.
Nobody owns the Bitcoin network much like no one owns the technology behind
email. Bitcoin is controlled by all Bitcoin users around the world. While
developers are improving the software, they can't force a change in the
Bitcoin protocol because all users are free to choose what software and
version they use. In order to stay compatible with each other, all users
need to use software complying with the same rules. Bitcoin can only work
correctly with a complete consensus among all users. Therefore, all users
and developers have a strong incentive to protect this consensus.
Forget most things you've heard. People discover Bitcoin in a variety of
ways, but usually pick up some sort of misconception like "Bitcoin gives
free money to people with computers" or "in order to use Bitcoin I have to
use a program that wastes electricity for nothing" along the way. Here is a
good summary to help you understand Bitcoin in general, by focusing on what
Bitcoin is and what problem it solves. These two things are not typically
well explained on most websites, and it is difficult to appreciate just how
effective a technology Bitcoin is until they are understood.
What Bitcoin is: An agreement amongst a community of people to use 21 million secure mathematical tokens--"bitcoins"--as money, like traditional African and Asian societies used the money cowry. Unlike the money cowry:
This is accomplished by the use of powerful cryptography many times stronger than that used by banks. Instead of simply being "sent" coins have to be cryptographically signed over from one entity to another, essentially putting a lock and key on each token so that bitcoins can be securely backed up in multiple places, and so that copying doesn't increase the amount you own.
Because bitcoins are given their value by the community, they don't need to be accepted by anyone else or backed by any authority to succeed. They are like a local currency except much, much more effective and local to the whole world. As an example of how effective the community is at "backing" the bitcoin: on April 4th 2011 30,000 bitcoins were abruptly sold on the largest Bitcoin exchange, consuming nearly all "buy" offers on the order book and dropping the price by nearly 1/3. But within a couple of days, the price on the exchange had fully rebounded and bitcoins were again trading at good volumes, with large "buy" offers slowly replacing the ones consumed by the trades. The ability of such a small economy (there were only 5 million out of the total 21 million bitcoins circulating then, or about 3.75 million USD worth at then-current exchange rates) to absorb such a large sell-off without crashing shows that bitcoins were already working beautifully.
What problem Bitcoin solves: Mathematically, the specific implementation of the bitcoin protocol solves the problem of "how to do all of the above without trusting anyone". If that sounds amazing, it should! Normally a local currency has to trust all kinds of people for it to be able to work. So does a national currency. And in both cases, that trust is often abused. But with Bitcoin, there's no one person who can abuse the system. Nobody can print more money, nobody can re-use the coins simply by making a copy, and nobody can use anyone else's coins without having direct access to their keys. People who break its mathematical "rules" simply end up creating a whole different system incompatible with the first. As long as these rules are followed by someone, the only way Bitcoin can fail is for everyone to stop using it.
This marvelous quality of not having to trust anyone is achieved in two ways. First, through the use of cutting-edge cryptography. Cryptography ensures that only the owner of the bitcoins has the authority to spend them. The cryptography used in Bitcoin is so strong that all the world's online banking would be compromised before Bitcoin would be, and it can even be upgraded if that were to start to happen. It's like if each banknote in your pocket had a 100-digit combination lock on it that couldn't be removed without destroying the bill itself. Bitcoin is that secure.
But the second way of securing the system, called the blockchain, is where the real magic happens. The blockchain is a single, authoritative record of confirmed transactions which is stored on the peer to peer Bitcoin network. Even with top-notch digital encryption, if there was no central registry to show that certain bitcoins had already been "paid" to someone else, you could sign over the same coins to multiple people in what's called a double-spend attack, like writing cheques for more money than you have in your account. Normally this is prevented by a central authority, the bank, who keeps track of all the cheques you write and makes sure they don't exceed the amount of money you have. Even so, most people won't accept a cheque from you unless they really trust you, and the bank has to spend a lot of money physically protecting those central records, whether they are kept in a physical or digital form. Not to mention, sometimes a bank employee can abuse their position of trust. And, in traditional banking, the bank itself doesn't have to follow the rules you do--it can lend out more money than it actually has.
The blockchain fixes all these problems by creating a single master registry of the already-cryptographically-secured bitcoin transfers, verifying them and locking them down in a highly competitive market called mining. In return for this critical role, the Bitcoin community rewards miners with a set amount of bitcoins per block, taken from the original limited quantity on a pre-agreed schedule. As that original amount gradually runs out, this reward will be replaced by fees paid to prioritise one transaction over another--again in a highly competitive market to ensure the lowest possible cost. The transactions are verified and locked in by the computational work of mining in a very special way so that no one else can change the official record of transactions without doing more computational work than the cumulative work of all miners across the whole network.
In conclusion: All this mathematical technology may be a bit of a mouthful, but what it means in practice is that Bitcoin works just like cash. Bitcoin transactions are intentionally irreversible--unlike credit cards or PayPal where chargebacks can invalidate a payment that has already been made. And there are no middlemen. Transactions are completed directly between the sender and the receiver via the peer to peer network.
Because of Bitcoin's intricate design, the network remains secure no matter where or how you process Bitcoin transactions. Which is incredible--no one else has ever tried to create a system that worked this way! All previous monetary systems have relied on trusting somebody, whether it was the king, town hall, the federal reserve, or banks. Bitcoin doesn't. It's guaranteed instead by the laws of mathematics, and that's why it has everyone from technologists to economists very excited. I'm sure you have lots more questions, so scan the index below to see if they've been asked before, then dive in! The so-called "canonical" threads linked from this index are considered newbie-friendly zones; outside of them you're welcome to try your own luck.
Copied from https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=7269.0.
What Bitcoin is: An agreement amongst a community of people to use 21 million secure mathematical tokens--"bitcoins"--as money, like traditional African and Asian societies used the money cowry. Unlike the money cowry:
- there will never be more bitcoins
- they are impossible to counterfeit
- they can be divided into as small of pieces as you want
- and they can be transferred instantly across great distances via a digital connection such as the internet.
This is accomplished by the use of powerful cryptography many times stronger than that used by banks. Instead of simply being "sent" coins have to be cryptographically signed over from one entity to another, essentially putting a lock and key on each token so that bitcoins can be securely backed up in multiple places, and so that copying doesn't increase the amount you own.
Because bitcoins are given their value by the community, they don't need to be accepted by anyone else or backed by any authority to succeed. They are like a local currency except much, much more effective and local to the whole world. As an example of how effective the community is at "backing" the bitcoin: on April 4th 2011 30,000 bitcoins were abruptly sold on the largest Bitcoin exchange, consuming nearly all "buy" offers on the order book and dropping the price by nearly 1/3. But within a couple of days, the price on the exchange had fully rebounded and bitcoins were again trading at good volumes, with large "buy" offers slowly replacing the ones consumed by the trades. The ability of such a small economy (there were only 5 million out of the total 21 million bitcoins circulating then, or about 3.75 million USD worth at then-current exchange rates) to absorb such a large sell-off without crashing shows that bitcoins were already working beautifully.
What problem Bitcoin solves: Mathematically, the specific implementation of the bitcoin protocol solves the problem of "how to do all of the above without trusting anyone". If that sounds amazing, it should! Normally a local currency has to trust all kinds of people for it to be able to work. So does a national currency. And in both cases, that trust is often abused. But with Bitcoin, there's no one person who can abuse the system. Nobody can print more money, nobody can re-use the coins simply by making a copy, and nobody can use anyone else's coins without having direct access to their keys. People who break its mathematical "rules" simply end up creating a whole different system incompatible with the first. As long as these rules are followed by someone, the only way Bitcoin can fail is for everyone to stop using it.
This marvelous quality of not having to trust anyone is achieved in two ways. First, through the use of cutting-edge cryptography. Cryptography ensures that only the owner of the bitcoins has the authority to spend them. The cryptography used in Bitcoin is so strong that all the world's online banking would be compromised before Bitcoin would be, and it can even be upgraded if that were to start to happen. It's like if each banknote in your pocket had a 100-digit combination lock on it that couldn't be removed without destroying the bill itself. Bitcoin is that secure.
But the second way of securing the system, called the blockchain, is where the real magic happens. The blockchain is a single, authoritative record of confirmed transactions which is stored on the peer to peer Bitcoin network. Even with top-notch digital encryption, if there was no central registry to show that certain bitcoins had already been "paid" to someone else, you could sign over the same coins to multiple people in what's called a double-spend attack, like writing cheques for more money than you have in your account. Normally this is prevented by a central authority, the bank, who keeps track of all the cheques you write and makes sure they don't exceed the amount of money you have. Even so, most people won't accept a cheque from you unless they really trust you, and the bank has to spend a lot of money physically protecting those central records, whether they are kept in a physical or digital form. Not to mention, sometimes a bank employee can abuse their position of trust. And, in traditional banking, the bank itself doesn't have to follow the rules you do--it can lend out more money than it actually has.
The blockchain fixes all these problems by creating a single master registry of the already-cryptographically-secured bitcoin transfers, verifying them and locking them down in a highly competitive market called mining. In return for this critical role, the Bitcoin community rewards miners with a set amount of bitcoins per block, taken from the original limited quantity on a pre-agreed schedule. As that original amount gradually runs out, this reward will be replaced by fees paid to prioritise one transaction over another--again in a highly competitive market to ensure the lowest possible cost. The transactions are verified and locked in by the computational work of mining in a very special way so that no one else can change the official record of transactions without doing more computational work than the cumulative work of all miners across the whole network.
In conclusion: All this mathematical technology may be a bit of a mouthful, but what it means in practice is that Bitcoin works just like cash. Bitcoin transactions are intentionally irreversible--unlike credit cards or PayPal where chargebacks can invalidate a payment that has already been made. And there are no middlemen. Transactions are completed directly between the sender and the receiver via the peer to peer network.
Because of Bitcoin's intricate design, the network remains secure no matter where or how you process Bitcoin transactions. Which is incredible--no one else has ever tried to create a system that worked this way! All previous monetary systems have relied on trusting somebody, whether it was the king, town hall, the federal reserve, or banks. Bitcoin doesn't. It's guaranteed instead by the laws of mathematics, and that's why it has everyone from technologists to economists very excited. I'm sure you have lots more questions, so scan the index below to see if they've been asked before, then dive in! The so-called "canonical" threads linked from this index are considered newbie-friendly zones; outside of them you're welcome to try your own luck.
Copied from https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=7269.0.
First, get yourself a bitcoin wallet
Your first step (for real this time) is to acquire a digital wallet to stash your future bitcoins in. Bitcoin wallets allow you to store, send and receive bitcoins. You can get one from an Internet-based wallet service, like Coinbase or Blockchain.info (for more click here).
Buy them from a Bitcoin exchange
At this time, the largest full trading exchanges are Localbitcoins, coinbase , CEX, BITSTAMP, Kraken, Bitfinex, Poloniex, HitBTC, GDAX and ShapeShift.
Your first step (for real this time) is to acquire a digital wallet to stash your future bitcoins in. Bitcoin wallets allow you to store, send and receive bitcoins. You can get one from an Internet-based wallet service, like Coinbase or Blockchain.info (for more click here).
Buy them from a Bitcoin exchange
At this time, the largest full trading exchanges are Localbitcoins, coinbase , CEX, BITSTAMP, Kraken, Bitfinex, Poloniex, HitBTC, GDAX and ShapeShift.
Three wonderful places where you can get your questions answered are the
Bitcoin Wiki at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bitcoin/
, the Bitcoin sub-reddit at Reddit.com/r/bitcoin
and Bitcoin Stack Exchange at Bitcoin.StackExchange.com
.
With our service, we understand that you may have a computer and a
smartphone device. It's 2014! You can connect up to three (3) devices
simultaneously with one (1) account.
Please visit the fallowing link : Restore
Account
At this time, this place has not been publicly on the site,please open a
support request.
You can switch an unlimited number of times between any country/gateway with
our VPN service.
Please visit the fallowing link : Restore
Account
We do not maintain any logs of any kind, period.
The best and easiest way is to visit a website that tells you your IP. The
best is ifconfig.me.you
can also visit WhatisMyIPAddress.com
. Your OpenVPN (Windows) or Tunnelblick (Mac OS X) should indicate
connectivity via the application icon as well.
That depends on the option Block the internet on connection failure. When it
is not selected protection is lost but the internet connection keeps
working. When it is selected the traffic destined for the tunnel will be
blocked until Disconnect or Quit is selected from the menu or until the
connection is reestablished.
We don't log our users' activities. When law requires us to divulge
information about our customers we make sure not to have that information
stored, so that we have nothing to give out.
However, credit card payments and Paypal transfers leave records. These are kept by the banks , paypal and card companies and can't be erased by us. To pay anonymously, use Bitcoin.
However, credit card payments and Paypal transfers leave records. These are kept by the banks , paypal and card companies and can't be erased by us. To pay anonymously, use Bitcoin.
One of the USA,United Kingdom
,Netherlands,Canada,Germany,France,Romania,Finland,Czech
Republic,Spain,Italy. You can choose which.
Reasonably fast in most cases but many things determine the speed so you
never know until you try.Fortunately it is free and very easy to try.please
open a support request.
Due to copyright laws, the use of anonymous servers only in the Netherlands
and Romania allowed.
The BitVPN Affiliate Program is a profitable deal for affiliates. It is an
extremely easy way to earn money by displaying BitVPN products, widgets and
links on your website, blog, forum etc. Once the promotion converts to sale,
the affiliates get paid a predetermined percentage commission.
Actually, you don't need any particular equipment or skill. The most
important is your motivation in making money by promoting our service.
You don't even need a website (although having your own website helps). You can promote BitVPN by adding our great variety of banners, or by sharing your affiliate link in an e-mail or a chat to someone you believe can make good use of our BitVPN platform to make a website for their business.
All you need to do is to send a visitor to our site via a special link (called 'affiliate link'), and if he or she buys anything from us, you will get up to 35% of the sale value.
You don't even need a website (although having your own website helps). You can promote BitVPN by adding our great variety of banners, or by sharing your affiliate link in an e-mail or a chat to someone you believe can make good use of our BitVPN platform to make a website for their business.
All you need to do is to send a visitor to our site via a special link (called 'affiliate link'), and if he or she buys anything from us, you will get up to 35% of the sale value.
Payments are issued via Bitcoin, also a minimum payout value of US$ 5
applies. We do not support paypal at the moment.
Payments are issued in Bitcoin (BTC) , and are paid each time you submit your request.
Payments are issued in Bitcoin (BTC) , and are paid each time you submit your request.
No. You can be an BitVPN affiliate with absolutely no costs.
Setting up an account is very easy and it's completely FREE. You don't have
to pay for becoming an affiliate.
To sign up just go to the Signup Form page and fill out your information. After you submit your information, you will receive an email message with a Activation link.
As our affiliate, you will have your own control panel where you can see detailed statistics of traffic and sales you referred, news and training materials, and a large choice of banners and text links to promote BitVPN.
Then you only need to place those affiliate links, banners, text links or other links at your web site so you can start sending customers to our web site.
To sign up just go to the Signup Form page and fill out your information. After you submit your information, you will receive an email message with a Activation link.
As our affiliate, you will have your own control panel where you can see detailed statistics of traffic and sales you referred, news and training materials, and a large choice of banners and text links to promote BitVPN.
Then you only need to place those affiliate links, banners, text links or other links at your web site so you can start sending customers to our web site.
An Affiliate link is a special URL where you should be sending the visitors.
You will get the URL's for different banners in your affiliate panel after
log in.
YES! You can promote us through pay-per-click in search engines. In fact,
this type of promotion becomes increasingly popular and we are aware of
several affiliates promoting BitVPN in this way. Just make sure that you add
your affiliate link in the online Ads.
We do not encourage keeping multiple affiliate accounts. It is strongly
recommended to maintain single affiliate account for better tracking
details.
Yes you can append same tracking ID on multiple websites, and that is how it
should be.
Tracing your accounting activity is now easy with a dedicated online panel
to track all your account activities.
1. Download the conection.zip and
extract zip file in your desktop.

2. Run the connections.pbk file.
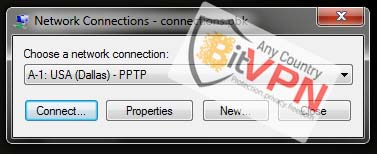
3. Select the protocol with required server. (all gateways included)
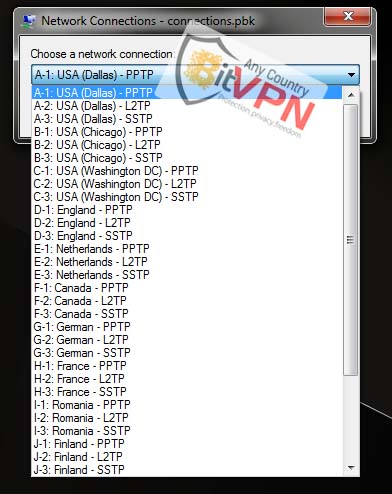
4. click on the Connect.
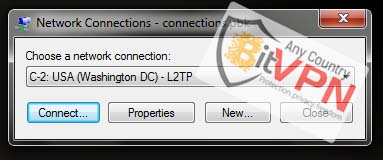
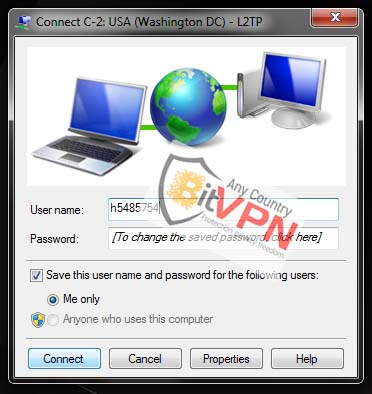
5. Enter username and password and click on the Connect.
6. Double click connections.pbk if you want to hang up a VPN connection.
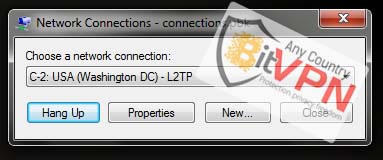
Note : This method will allow you to connect to BitVPN using PPTP and SSTP, however, for LT2P first you would need run "L2TP.reg" and restart your windows. And perform the following steps

2. Run the connections.pbk file.

3. Select the protocol with required server. (all gateways included)

4. click on the Connect.

5. Enter username and password and click on the Connect.

6. Double click connections.pbk if you want to hang up a VPN connection.

Note : This method will allow you to connect to BitVPN using PPTP and SSTP, however, for LT2P first you would need run "L2TP.reg" and restart your windows. And perform the following steps
L2TP on Mac OS X
1. Open System Preferences
2. Open Network
3. Click on Create new Service
4. Select an interface, VPN type and enter a name for the service and click Create
Interface: VPN
VPN Type: L2TP over IPSec
Service Name: BitVPN l2tp (or other name to help you identify the connection)
5. You new VPN connection should now appear in the left column. Select it and enter the following settings:
Server address: hostname or IP address of the VPN Node you want to connect to. (Full List)
Account name: your VPN username
Check Show VPN status in menu bar
6. Open Authentication Settings... and enter vpn2key in the Shared Secret field. CLick OK to return
7. Click Advanced and make sure you check Send all traffic over VPN connection and click OK. Otherwise you will connect to the VPN but you won't exit through our VPN Node. Click OK to return
8. Now click on Apply and Connect. You will be asked to insert your VPN password
9. Once connected, you will see the connection status
10. To disconnect, click on VPN connection status in Menu Bar and click Disconnect BitVPN l2tp
------------------------------------------------------------
PPTP on Mac OS X
1. Open System Preferences
2. Open Network
3. Click on Create new Service
4. Select an interface, VPN type and enter a name for the service and click Create
Interface: VPN
VPN Type: L2TP over IPSec
Service Name: BitVPN pptp (or other name to help you identify the connection)
5. You new VPN connection should now appear in the left column. Select it and enter the following settings:
Server address: hostname or IP address of the VPN Node you want to connect to. (Full List)
Account name: your VPN username
Encryption: None
Check Show VPN status in menu bar
6. Click Advanced and make sure you check Send all traffic over VPN connection and click OK. Otherwise you will connect to the VPN but you won't exit through our VPN Node.
7. Now click Apply and Connect. You will be asked to insert your password
8. Once connected, you will see the connection status
9. To disconnect, click on VPN connection status in Menu Bar and click Disconnect BitVPN pptp
1. Open System Preferences
2. Open Network
3. Click on Create new Service
4. Select an interface, VPN type and enter a name for the service and click Create
Interface: VPN
VPN Type: L2TP over IPSec
Service Name: BitVPN l2tp (or other name to help you identify the connection)
5. You new VPN connection should now appear in the left column. Select it and enter the following settings:
Server address: hostname or IP address of the VPN Node you want to connect to. (Full List)
Account name: your VPN username
Check Show VPN status in menu bar
6. Open Authentication Settings... and enter vpn2key in the Shared Secret field. CLick OK to return
7. Click Advanced and make sure you check Send all traffic over VPN connection and click OK. Otherwise you will connect to the VPN but you won't exit through our VPN Node. Click OK to return
8. Now click on Apply and Connect. You will be asked to insert your VPN password
9. Once connected, you will see the connection status
10. To disconnect, click on VPN connection status in Menu Bar and click Disconnect BitVPN l2tp
------------------------------------------------------------
PPTP on Mac OS X
1. Open System Preferences
2. Open Network
3. Click on Create new Service
4. Select an interface, VPN type and enter a name for the service and click Create
Interface: VPN
VPN Type: L2TP over IPSec
Service Name: BitVPN pptp (or other name to help you identify the connection)
5. You new VPN connection should now appear in the left column. Select it and enter the following settings:
Server address: hostname or IP address of the VPN Node you want to connect to. (Full List)
Account name: your VPN username
Encryption: None
Check Show VPN status in menu bar
6. Click Advanced and make sure you check Send all traffic over VPN connection and click OK. Otherwise you will connect to the VPN but you won't exit through our VPN Node.
7. Now click Apply and Connect. You will be asked to insert your password
8. Once connected, you will see the connection status
9. To disconnect, click on VPN connection status in Menu Bar and click Disconnect BitVPN pptp
1. Click on the Network Manager icon, go to VPN Connections > Configure
VPN...
2. In the Network Manager window (VPN tab), click + Add
3. Leave Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) selected or select it if there are more VPN protocols in the list then click Create...
4. In the connection editor window, enter the following:
Connection name: a unique name such as BitVPN pptp
Gateway: hostname or IP address of the VPN node you want to connect to. (Full List)
Username and Password: your VPN username and your VPN password
Depending on your preferences, you may want to check or uncheck the Available to all users button
After you enter the details above, click on Advanced...
5. In the PPTP Advanced Options window:
- leave only CHAP checked (uncheck the others)
- check Use Allow BSD data compression
- check Use Allow Deflate data compression
- check Use Use TCP header compression
- uncheck other options
6. Click OK to return to the previous window, then click Save...
Now you should find the new VPN connection when you access the Network Manager icon
7. Click on the VPN connection name to connect. A notification message will appear in the upper-right corner in a few seconds
2. In the Network Manager window (VPN tab), click + Add
3. Leave Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) selected or select it if there are more VPN protocols in the list then click Create...
4. In the connection editor window, enter the following:
Connection name: a unique name such as BitVPN pptp
Gateway: hostname or IP address of the VPN node you want to connect to. (Full List)
Username and Password: your VPN username and your VPN password
Depending on your preferences, you may want to check or uncheck the Available to all users button
After you enter the details above, click on Advanced...
5. In the PPTP Advanced Options window:
- leave only CHAP checked (uncheck the others)
- check Use Allow BSD data compression
- check Use Allow Deflate data compression
- check Use Use TCP header compression
- uncheck other options
6. Click OK to return to the previous window, then click Save...
Now you should find the new VPN connection when you access the Network Manager icon
7. Click on the VPN connection name to connect. A notification message will appear in the upper-right corner in a few seconds
L2TP/IPSec on Android
1. Go to Settings > Wireless & Networks > More... and select VPN
2. If you are warned to set a lock screen PIN or password before you can use credentials storage, tap ok
3. In the Unlock Selection settings, use your preferred method to unlock the phone (pattern, PIN, password)
4. Now you will be able to open the VPN connections list where you should tap on the + sign in the upper-right corner
5. Now you will add a new VPN Profile:
Name: enter an unique name for this connection, such as BitVPN l2tp
Type: L2TP/IPSec PSK
Server address: VPN Node address (Full List)
L2TP secret: (not used)
IPSec identifier: (not used)
IPSec pre-shared key: vpn2key
Tap on Save
6. Your new L2TP/IPSec VPN profile was created. Open it and you will be asked for your VPN username and password. You may want to Save account information. Tap on Connect
7. If everything was ok, you are now connected
8. The VPN Connection icon will remain active in the notifications bar. Open it and tap on Disconnect when you want to disconnect from the VPN
------------------------------------------------------------
PPTP on Android
1. Go to Settings > Wireless & Networks > More... and select VPN
2. If you are warned to set a lock screen PIN or password before you can use credentials storage, click ok
3. In the Unlock Selection settings, use your preferred method to unlock the phone (pattern, PIN, password)
4. Now you will be able to open the VPN connections list where you should tap on the + sign in the upper-right corner
5. Now you will add a new VPN Profile:
Name: enter an unique name for this connection, such as BitVPN pptp
Type: PPTP
Server address: the VPN node hostname or IP address. (Full List)
PPP encryption (MPPE): make sure it is uncheck, then tap on Save
6. Your new PPTP VPN profile was created. Open it and you will be asked for your VPN username and password. You may want to Save account information. Tap on Connect
7. If everything was ok, you are now connected.
8. If you open the Status bar to select the VPN connection, a status window will appear. Tap on Disconnect when you want to close your VPN connection
1. Go to Settings > Wireless & Networks > More... and select VPN
2. If you are warned to set a lock screen PIN or password before you can use credentials storage, tap ok
3. In the Unlock Selection settings, use your preferred method to unlock the phone (pattern, PIN, password)
4. Now you will be able to open the VPN connections list where you should tap on the + sign in the upper-right corner
5. Now you will add a new VPN Profile:
Name: enter an unique name for this connection, such as BitVPN l2tp
Type: L2TP/IPSec PSK
Server address: VPN Node address (Full List)
L2TP secret: (not used)
IPSec identifier: (not used)
IPSec pre-shared key: vpn2key
Tap on Save
6. Your new L2TP/IPSec VPN profile was created. Open it and you will be asked for your VPN username and password. You may want to Save account information. Tap on Connect
7. If everything was ok, you are now connected
8. The VPN Connection icon will remain active in the notifications bar. Open it and tap on Disconnect when you want to disconnect from the VPN
------------------------------------------------------------
PPTP on Android
1. Go to Settings > Wireless & Networks > More... and select VPN
2. If you are warned to set a lock screen PIN or password before you can use credentials storage, click ok
3. In the Unlock Selection settings, use your preferred method to unlock the phone (pattern, PIN, password)
4. Now you will be able to open the VPN connections list where you should tap on the + sign in the upper-right corner
5. Now you will add a new VPN Profile:
Name: enter an unique name for this connection, such as BitVPN pptp
Type: PPTP
Server address: the VPN node hostname or IP address. (Full List)
PPP encryption (MPPE): make sure it is uncheck, then tap on Save
6. Your new PPTP VPN profile was created. Open it and you will be asked for your VPN username and password. You may want to Save account information. Tap on Connect
7. If everything was ok, you are now connected.
8. If you open the Status bar to select the VPN connection, a status window will appear. Tap on Disconnect when you want to close your VPN connection
L2TP on iOS
1. Go to the Home Screen by pressing the Home Button on your device
2. Open the Settings menu
3. In the Settings Menu, Select General then VPN. If you are already using VPN connections on your iOS device, the VPN menu will be visible in the main Settings Menu.
4. Select Add VPN Configuration
5. In the following dialog, select the appropriate connection type from the options above: L2TP
6. Enter the login details you have received by e-mail, from BitVPN, in the configuration dialog, as follows:
Server - Enter the server address you want to establish a connection to. (Full List)
Account - Your VPN username
Password - Your VPN password
Encryption Level - This must be set to Auto
Secret - The Preshare Key used by all BitVPN connections: vpn2key
Send All Traffic - ON
Click on the Save button in the top right-hand corner to save all changes and get back to the VPN Menu
7. After entering the connection details, as described above, you will return to the VPN Menu.
8. Slide the VPN switch in the ON position to connect to BitVPN
9. Once the connection is established, the VPN icon will appear on the status bar. To disconnect from VPN, Go to the Settings Menu - VPN and slide the Connection button to the Off Position
------------------------------------------------------------
PPTP on iOS
1. Go to the Home Screen by pressing the Home Button on your device
2. Open the Settings menu
3. In the Settings Menu, Select General then VPN. If you are already using VPN connections on your iOS device, the VPN menu will be visible in the main Settings Menu.
4. Select Add VPN Configuration
5. In the following dialog, select the appropriate connection type from the options above: PPTP
6. Enter the login details you have received by e-mail, from BitVPN, in the configuration dialog, as follows:
Server - Enter the server address you want to establish a connection to. (Full List)
Account - Your VPN username
Password - Your VPN password
Encryption Level - This must be set to Auto
Send All Traffic - ON
Click on the Save button in the top right-hand corner to save all changes and get back to the VPN Menu
7. After entering the connection details, as described above, you will return to the VPN Menu.
8. Slide the VPN switch in the ON position to connect to BitVPN
9. Once the connection is established, the VPN icon will appear on the status bar. To disconnect from VPN, Go to the Settings Menu - VPN and slide the Connection button to the Off Position
1. Go to the Home Screen by pressing the Home Button on your device
2. Open the Settings menu
3. In the Settings Menu, Select General then VPN. If you are already using VPN connections on your iOS device, the VPN menu will be visible in the main Settings Menu.
4. Select Add VPN Configuration
5. In the following dialog, select the appropriate connection type from the options above: L2TP
6. Enter the login details you have received by e-mail, from BitVPN, in the configuration dialog, as follows:
Server - Enter the server address you want to establish a connection to. (Full List)
Account - Your VPN username
Password - Your VPN password
Encryption Level - This must be set to Auto
Secret - The Preshare Key used by all BitVPN connections: vpn2key
Send All Traffic - ON
Click on the Save button in the top right-hand corner to save all changes and get back to the VPN Menu
7. After entering the connection details, as described above, you will return to the VPN Menu.
8. Slide the VPN switch in the ON position to connect to BitVPN
9. Once the connection is established, the VPN icon will appear on the status bar. To disconnect from VPN, Go to the Settings Menu - VPN and slide the Connection button to the Off Position
------------------------------------------------------------
PPTP on iOS
1. Go to the Home Screen by pressing the Home Button on your device
2. Open the Settings menu
3. In the Settings Menu, Select General then VPN. If you are already using VPN connections on your iOS device, the VPN menu will be visible in the main Settings Menu.
4. Select Add VPN Configuration
5. In the following dialog, select the appropriate connection type from the options above: PPTP
6. Enter the login details you have received by e-mail, from BitVPN, in the configuration dialog, as follows:
Server - Enter the server address you want to establish a connection to. (Full List)
Account - Your VPN username
Password - Your VPN password
Encryption Level - This must be set to Auto
Send All Traffic - ON
Click on the Save button in the top right-hand corner to save all changes and get back to the VPN Menu
7. After entering the connection details, as described above, you will return to the VPN Menu.
8. Slide the VPN switch in the ON position to connect to BitVPN
9. Once the connection is established, the VPN icon will appear on the status bar. To disconnect from VPN, Go to the Settings Menu - VPN and slide the Connection button to the Off Position
1. Download the OpenVPN Windows
Installer
2. Run the installer and click Ok or Yes if any Security Warnings appear.
3. Continue and write down the installation folder path.
4. Download the OpenVPN Configuration files.
5. Extract the files from the zip and copy all of the configuration files to the config folder found in the installation path from Step 3 (Usually C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\config or C:\Program Files (x86)\OpenVPN\config).
6. Windows 7 and Vista users will need to right click on the OpenVPN shortcut on the desktop and choose Properties and enable Run this program as an administrator.
7. Connect by right clicking the OpenVPN System Tray Icon, navigating to the server and choosing connect. When you are prompted, enter your username and password.
2. Run the installer and click Ok or Yes if any Security Warnings appear.
3. Continue and write down the installation folder path.
4. Download the OpenVPN Configuration files.
5. Extract the files from the zip and copy all of the configuration files to the config folder found in the installation path from Step 3 (Usually C:\Program Files\OpenVPN\config or C:\Program Files (x86)\OpenVPN\config).
6. Windows 7 and Vista users will need to right click on the OpenVPN shortcut on the desktop and choose Properties and enable Run this program as an administrator.
7. Connect by right clicking the OpenVPN System Tray Icon, navigating to the server and choosing connect. When you are prompted, enter your username and password.
1. Download the Tunnelblick from Sourceforge
2. Download the OpenVPN Configuration files. TCP Config / UDP Config
3. Extract configuration files from the zip.
4. Open the Tunnelblick DMG
5. Double click on the Tunnelblick Icon.
6. After installation has completed, launch Tunnelblick.
7. When you see a dialogue box with an option to Create and open configuration folder, choose this option.
8. Copy the files extracted in Step 3 to this folder.
9. Connect by right clicking the Tunnelblick icon in the menubar.
10. When you are prompted, enter your username and password.
2. Download the OpenVPN Configuration files. TCP Config / UDP Config
3. Extract configuration files from the zip.
4. Open the Tunnelblick DMG
5. Double click on the Tunnelblick Icon.
6. After installation has completed, launch Tunnelblick.
7. When you see a dialogue box with an option to Create and open configuration folder, choose this option.
8. Copy the files extracted in Step 3 to this folder.
9. Connect by right clicking the Tunnelblick icon in the menubar.
10. When you are prompted, enter your username and password.
Download the tutorial for linux from here
1. Download and install the kerio Client.
2. Run the software and enter the server address that you want to connect, such us5.koadd.com
(without a word at the beginning and end)
3. type username and password and click on the Connect.
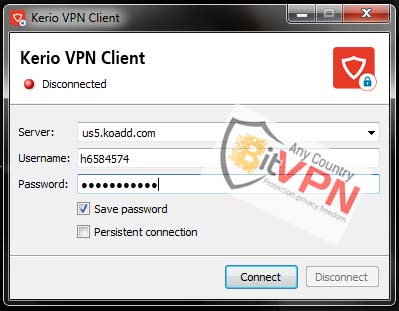
2. Run the software and enter the server address that you want to connect, such us5.koadd.com
(without a word at the beginning and end)
3. type username and password and click on the Connect.

